In this quick tutorial, we’ll explain how to enable ASLR for added protection against security threats.
ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomization) is a security technique that was originally used on GNU/Linux systems. However, these days, it’s used by many operating systems as an additional form of protection against certain attacks.
What this technique does is randomise the location where system executables, libraries or memory stacks are loaded in the system memory.
Hackers often try to exploit systems by guessing the location of important data or executables. By randomising everything, it makes it much harder for a hacker to take control of the system or exploit data.
Before you get started
To successfully complete this tutorial, you will need the following:
- To be registered with an organisation on the Jotelulu platform and have logged in.
- To have an active Servers subscription.
How to Enable ASLR
First, click on the search bar and type “Virus and threat protection” (1), although “virus” will probably be enough for the system to begin displaying results.
From the results displayed, click on “Virus and threat protection” (2).
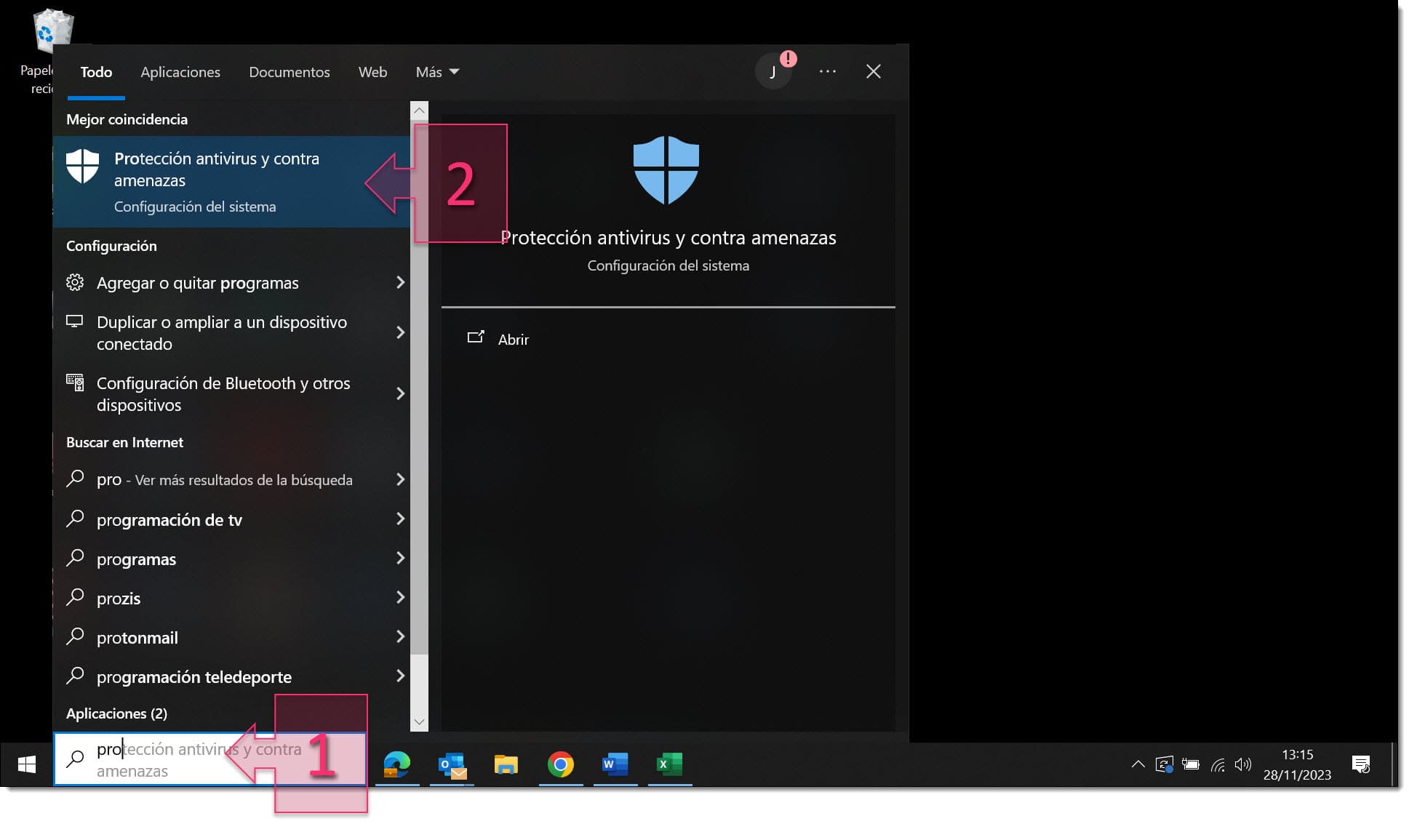
You will then see the Windows Security console.
On the left-hand side, click on “App & browser control” (3).
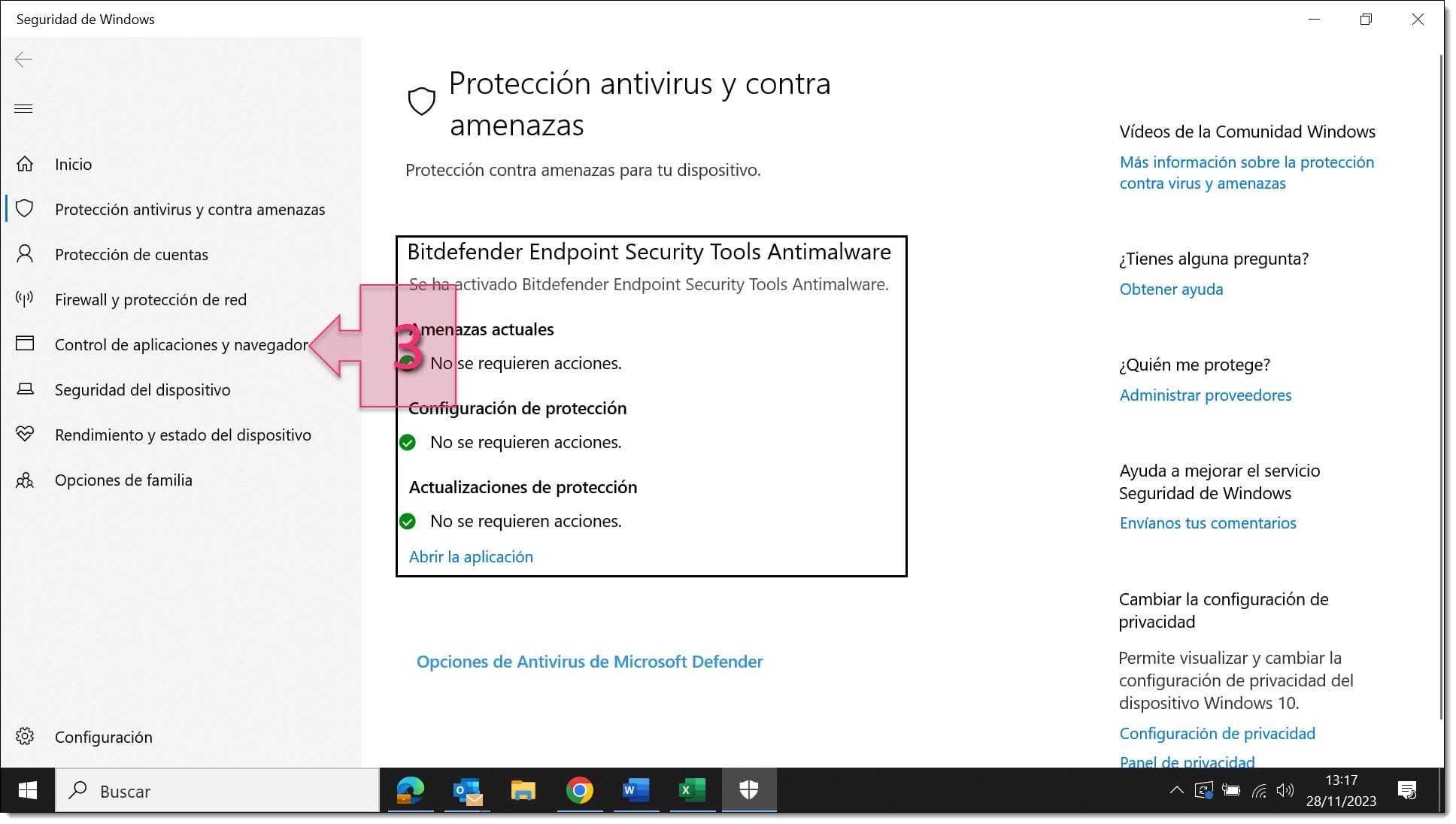
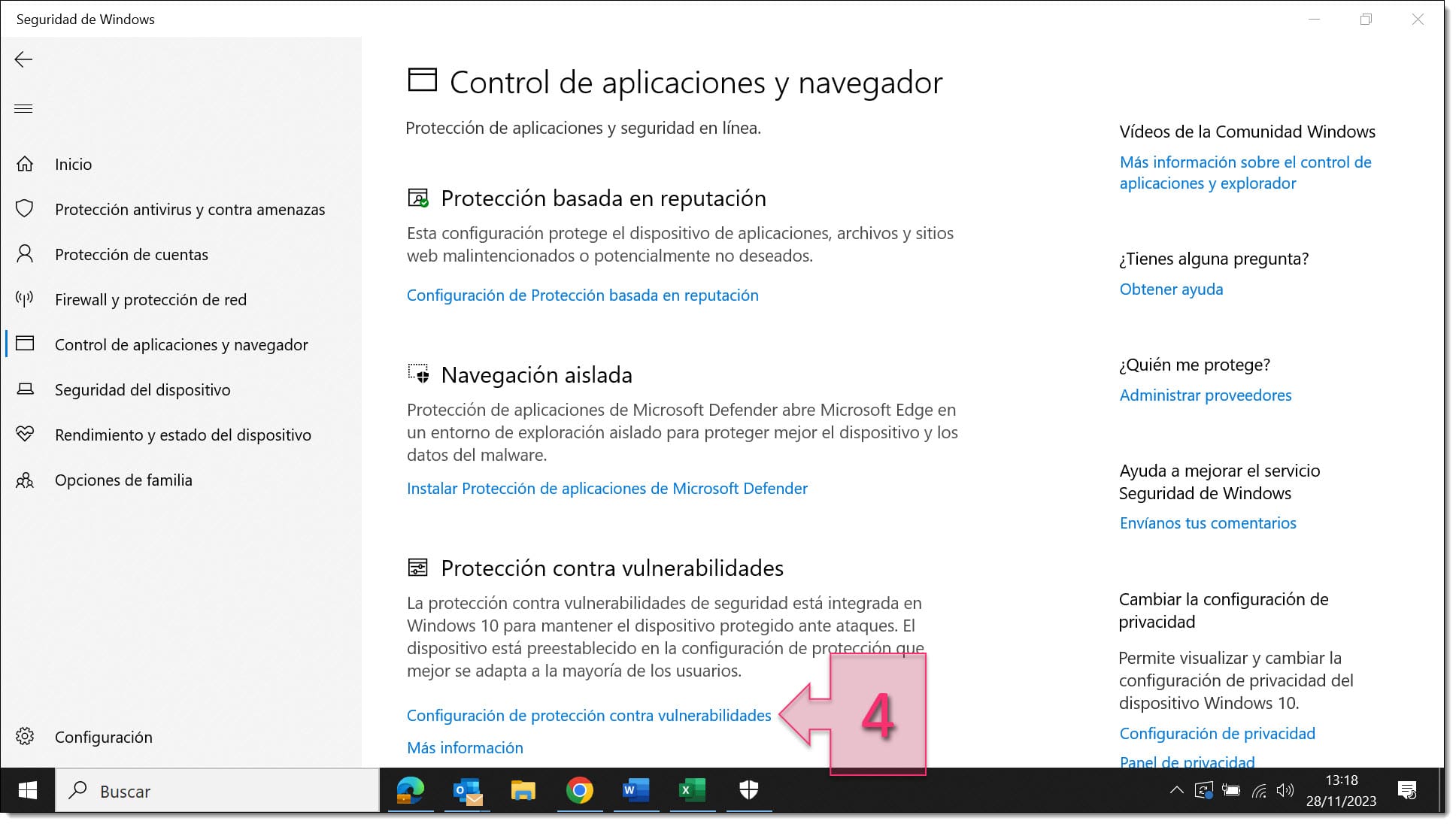
Then, on the App & browser control screen, below “Exploit protection” , click on “Exploit protection settings” (4).
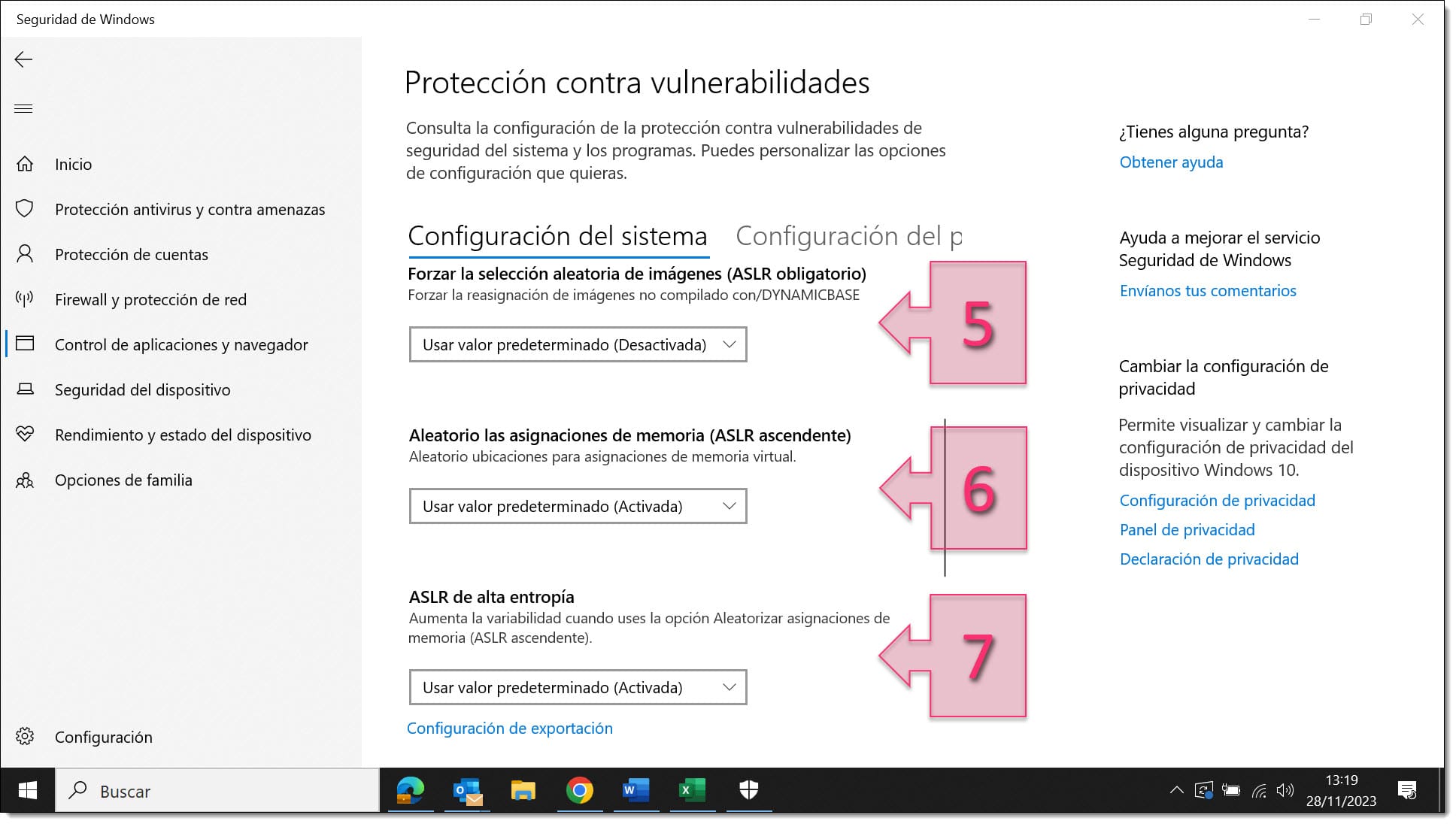
On the next screen, you will see three settings related to ASLR which you can freely enable or disable:
- Force randomisation for images (Mandatory ASLR) (5)
- Randomise memory allocations (Bottom-up ASLR) (6): Used to randomise virtual memory allocations, including memory stacks, the Thread Environment Block (TEB) and the Process Environment Block (PEB).
- High-entropy ASLR (7): This option notably increases the randomisation by adding more bits, thereby increasing security.
NOTE: Some apps may experience issues when you enable ASLR, so you may have to disable it to avoid problems.
Summary
In this tutorial, we’ve shown how easy it is to enable ASLR on your Windows system. This technique randomises the memory location of key data and processes, thereby providing increased protection against cyberattacks.
This feature is available on both Microsoft Windows Client systems, such as Windows 10 or 11, and Windows Server, such as Windows Server 2022 and some earlier versions.
As you can see, it’s a really simple process, so there’s no excuse for not enabling it!
We also recommend that you check out our blog for other similar tutorials and articles.
Thanks for choosing Jotelulu!





